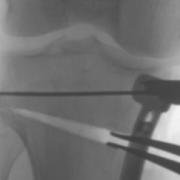
Laminar spreaders open the wedge of a high tibial osteotomy.
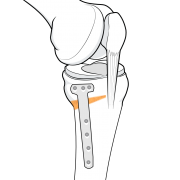
The re-aligned bone is held in the new position with a plate and screws until new bone fills the gap.
High tibial osteotomy is a surgical procedure where the bone of the upper tibia is cut and re-angled to change the limb alignment. Page updated October 2023 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)

Laminar spreaders open the wedge of a high tibial osteotomy.

The re-aligned bone is held in the new position with a plate and screws until new bone fills the gap.
The most common reasons for a surgeon to offer realignment surgery such as high tibial osteotomy include:
The osteotomy surgeon will be meticulous in planning the exact amount of change of alignment required, and whether the adjustment requires an opening wedge or a closing wedge. For this, the patient will be ushered to the X-ray department and long leg X-rays will be taken, to include the pelvis and feet.
Usually a high tibial osteotomy is performed to correct a varus (bow-legged) deformity, and the correction is made via an 'opening wedge'. Occasionally a closing wedge is indicated, and the site and degree of correction is nowadays determined by computer evaluation of weight-bearing full leg X-rays.
A double osteotomy or a double-level osteotomy is when the bone both above and below the knee joint are re-angled via osteotomy, ie a high tibial osteotomy below the joint and a distal femoral osteotomy above the joint.
A short discussion about noises in the plated knee.
Discussion about the first three weeks after an osteotomy.
An anxious patient wants to learn more before moving from the unloader brace to a high tibial osteotomy..
About rehab and regaining range of knee motion after HTO hardware removal.
High Tibial Osteotomy for Varus Deformity of the Knee
Citation: Murray R, Winkler PW, Shaikh HS, Musahl V. High Tibial Osteotomy for Varus Deformity of the Knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2021 Jul 9;5(7):e21.00141. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00141. PMID: 34242204; PMCID: PMC8274793.